Drupal 8: Multilingual Features
Drupal is a comprehensive, open-source content management system (CMS). It is becoming one of the most favorable CMSs among global enterprises, higher education institutions, governments and NGOs. Drupal 8 comes with many new features and improvements; I will discuss the multilingual features in this blog.
Drupal 8 can be installed in 94 languages, it also supports multilingual features right out of the box, providing four core modules specifically for language support and translation.
The admin interface has built-in translations. You can also create pages with language-based view filtering and block visibility. Translation updates from the community are automatically facilitated.
Below are the four core modules that support translation:

Configuration Translation
This module allows configuration to be translated into different languages. Through this module, translation of views, site name, contact module categories, vocabularies, menus, blocks and more can be translated.
Content Translation
Content is translatable using the core content translation module. It is similar to the “Entity Translation” approach in Drupal 7.
If you need to translate content, enable this module in configuration.
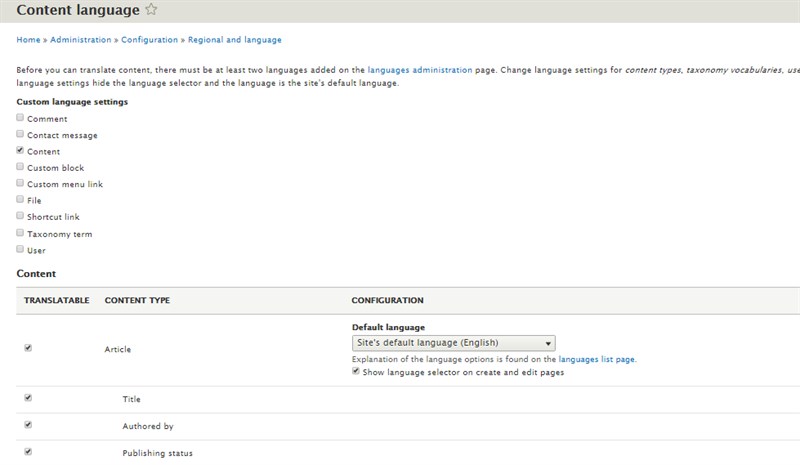
To do this, you need to first decide which entity type you want to make translatable (comments, contact message, content etc.), then within each entity type, you need to select which sub-types will be translated (title, tags, body etc.). For each sub-type, select which fields will be translated.
In the content page, you can see “Translate” in the drop-down menu next to any content type.
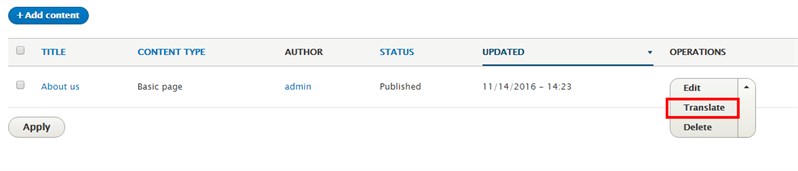
Selecting “Translate” takes you to the translate tab, shown below, where you can add any language translation to selected content type.
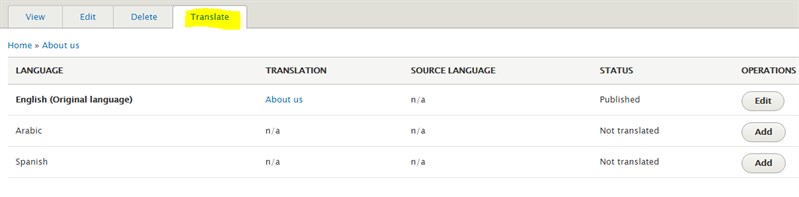
To add a new translation for a specific language, click “Add” on the selected language. In this case, I have selected “Arabic”. Drupal detects automatically that Arabic is RTL and the layout is modified accordingly.
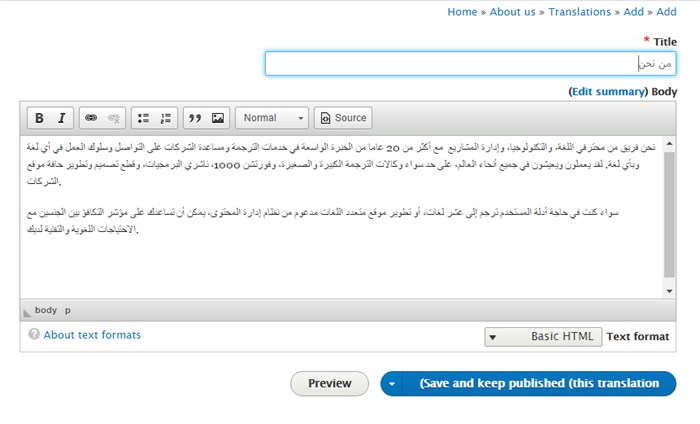
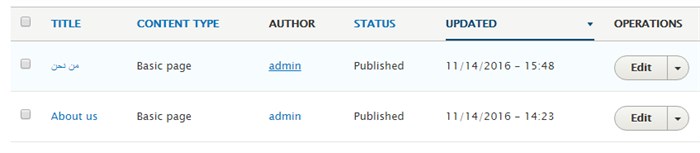
The original content is displayed in fields for you to replace with translations. Once done, you can save and publish. Now the newly added page is listed under the content tab, show below.
Languages
Some new improvements in Drupal 8 include:
- Language can be assigned to everything: nodes, users, views, blocks, menus.
- Better language selection defaults (URL negotiation enabled by default).
- Browser language detection is configurable with external language codes.
- Newly configurable fallback language.
- An admin interface language selection option per user.
- Transliteration is built-in for machine names.
To be able to translate any of your content to a specific language, you need to enable the selected language from the languages section in the configuration page.
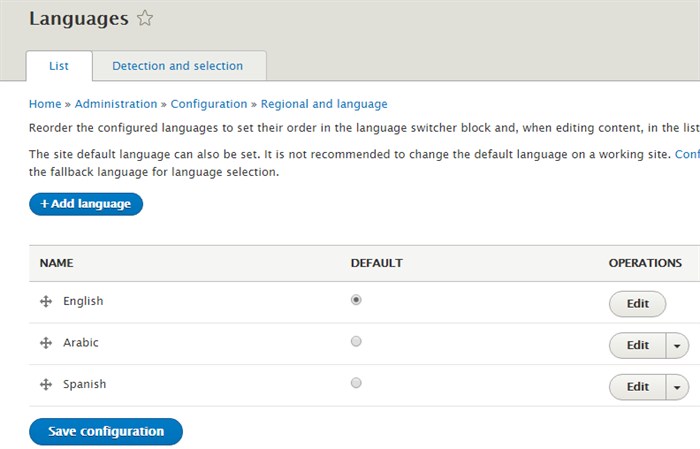
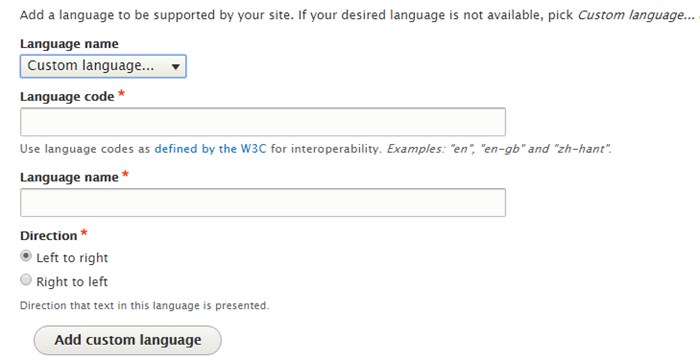
You can select any language from a wide range of languages out of the box. Or define a custom language if you didn’t find the target language in the existing options.
Interface Translation
Interface translation (known as locale in previous versions) translates the built-in user interface. One major improvement is that English doesn’t need to be installed, it also became customizable/removable.
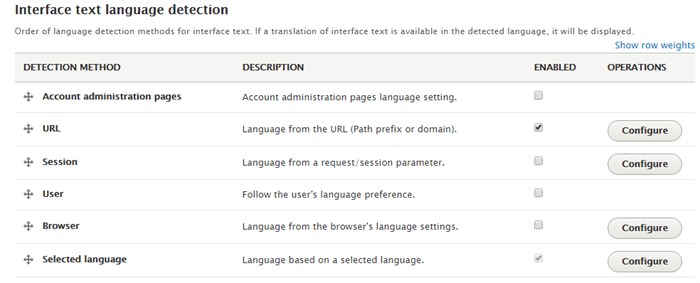
To decide how a language is detected to display page elements, follow the below steps:
Configuration >> Regional and Language >> Languages