Translation and Localization Quality Management – LQA Standard and LQA Metrics
To evaluate the quality and productivity of translation and localization companies need an objective approach to keep up with the industry standards and metrics. A standard is a required or agreed level of quality while a metric is a system of measurement that shows that a service or a product complies with an agreed level of quality. In this blog, I’m going to share with you the standards and metrics used in Translation Quality Management.
Translation and Localization Quality Standard
ISO 17100
 ISO 17100:2015 details the requirements for the fundamental processes, resources, and other criteria necessary for the delivery of a quality translation service that meets established standards. Application of ISO 17100:2015 provides the means that a translation service provider (TSP) can demonstrate the conformity of translation services to ISO 17100:2015. A company that is ISO certified has adopted the universal best practices established and has been reviewed and certified that it follows these standards. This certification should provide a buyer of translation services the assurance that the TSP is committed to delivering a translation service that will meet the client’s specifications.
ISO 17100:2015 details the requirements for the fundamental processes, resources, and other criteria necessary for the delivery of a quality translation service that meets established standards. Application of ISO 17100:2015 provides the means that a translation service provider (TSP) can demonstrate the conformity of translation services to ISO 17100:2015. A company that is ISO certified has adopted the universal best practices established and has been reviewed and certified that it follows these standards. This certification should provide a buyer of translation services the assurance that the TSP is committed to delivering a translation service that will meet the client’s specifications.
ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001 defines the objectives of the Quality Management System (QMS) and its policies, and requirements related to documentation control, purchasing, working with subcontractors, human resources, internal quality audits, handling non-conformities, and other internal operations. By selecting an ISO 9001-certified company, you can be assured that the company is dedicated to its quality system and is serious about quality.
ISO 18587:2017
This is a relatively new, translation-industry-specific standard that deals with Post-Editing Machine Translation (PEMT). The standard provides requirements for the process of full, human post-editing of machine translation output and post-editor competencies, and it makes PEMT more acceptable and mainstream.
ISO 13485:2016
ISO 13485:2016 is a standard that’s specific to the medical industry, including medical devices and related services. It specifies requirements for a quality management process that asks a medical company to provide medical devices and services that consistently meet applicable regulatory requirements.
Linguistic Quality Assurance (LQA)
Linguistic Quality Assurance (LQA) is indispensable for collecting objective feedback and examining translation quality, at any given point in time.
Traditional LQA metrics, such as the LISA QA model and SAE J2450 mainly focused on technical accuracies such as terminology, mistranslations, omissions, and additions. TAUS’ DQF-MQM Error Typology still applies the best parts of the existing metrics and expands its categories and adds metrics, including fluency, style, and severity.
The LISA QA Model
The LISA QA Model, was created by the Localization Industry Standards Association (LISA), has been used as a metric to assess translation quality and count errors to determine whether the target content meets the requirements. The Lisa QA Model v3.1, introduced in the 1990s, which was an error rating model. LISA QA rates an error according to its severity and the corresponding weight, including minor, major, and critical with points of 1, 5, and 10 respectively for each error type. The model records both linguistic and technical errors. Utilizing the LISA QA Model assists to ensure the consistency of terminology and content.
MQM (Multidimensional Quality Metrics)
MQM is a flexible system providing translation assessment metrics compared to the models above. It can be used to evaluate the source content which also affects the quality of the final translation based on quality enablement. Besides, the MQM QA model can evaluate not only human translation but also machine translation.
MQM includes over 100 issue types. For the top level, there are eight major categories/branches: Accuracy, Fluency, Terminology, Locale convention, Style, Verity, Design, and Internationalization. It’s also extensible and allows companies to customize their preferred categories based on the content types and subject matters.
The MQM-DQF Harmonized Metric

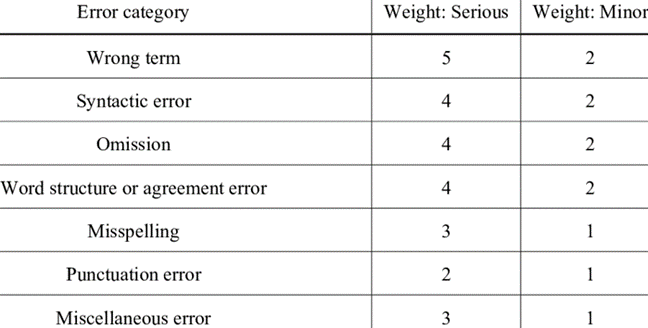
SAE J2450 is a statistical tool that automakers use to grade document translation quality according to seven error types, including the wrong term, syntactic error, omission, word structure or agreement error, misspelling, punctuation error, and miscellaneous error. The purpose of SAE J2450 was to create a consistent standard to evaluate the quality of automotive service information translations. This metric can be applied to either human translation or machine translation.
Conclusion
Currently, most of the CAT tools and TMS tend to integrate with a QA model or QA functions which helps language service providers deliver projects at a full scale with compliance to ISO 17100:2015. For example, when the reviewers find issues or errors, they will be asked to select the issue category and severity level with their comments. The final report will be generated based on the issue type and severity which allows the LPMs to check the translation quality and seek improvement plans. Therefore, translation and localization professionals should understand the LQA standards, LQA metrics, and how they are applied and work to ensure the best translation and localization practices.
