Japanese Website Translation Basics
For the last few decades, getting a foothold in the Japanese market has proven difficult for foreign firms. The internet has helped to open the gates to this very interesting and complex market. Despite most of the population having studied English as part of their formal education, the Japanese people overwhelming prefer to visit sites that are truly Japanese in style and content. Still many companies fail to recognize the importance of fully localizing and customizing the website experience for the Japanese consumer. Attracting the right Japanese consumer and keeping them loyal has never been more difficult.
Big in Japan
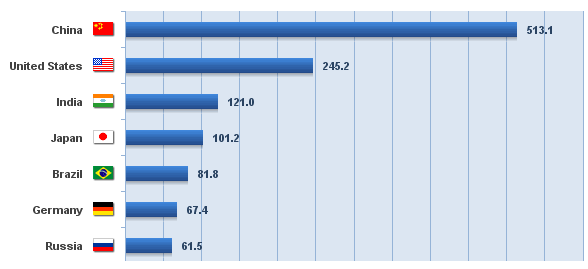
Although Japan’s economy continues to face challenges, it still ranks among one of the leaders in the world. It boasts over a 98% literacy rate and a citizenry known for its work ethic and devotion to lifetime employment at a single employer (though this has changed in recent years). Furthermore, the Japanese are technophiles. This technologically advanced society is an early adopter and heavy consumer of the bleeding-edge electronics. According to Internet World Stats (Internet World Stats, June 2012), Japan boasts over 101 million users (~80% of the population) and growing.
Worldwide Top Internet Countries – Q2 2012 (users in millions)

Japan’s Mobile Market
Smartphone usage across Asia continues to grow at leaps and bounds. Japan raced to a leadership position years ago and continues to demonstrate an unusual propensity to use handheld devices. When creating the information architecture for website content, organizations addressing the Japanese market must comprehend how to communicate using this smaller form factor. Smartphone use is on the rise in the US, the UK, France, Germany and Japan according to a study conducted by Google on Daily Internet Usage (2011).

The Japanese users reach first for their smartphones when accessing internet content. Google continues to provide valuable insight into this market with their Our Mobile Planet 2012 Research. This research yielded that “77% of Japanese smartphone users have used their phone every day in the past 7 days, which is the highest among the 26 countries around the word.” When queried on the most common activities performed on mobile devices, 68% of Japanese indicate that they are using their smartphone for mobile search. It is clear that consumers are dependent on their mobile devices and companies need to recognize its importance.
The Japanese Language
Japanese is an East Asian language spoken by about 125 million speakers, primarily in Japan, where it is the national language. It is a member of the Japonic (or Japanese-Ryukyuan) language family, whose relation to other language groups is debated.
Japanese is an agglutinative, mora-timed language with simple phonotactics, a pure vowel system, phonemic vowel and consonant length, and a lexically significant pitch-accent. Word order is normally subject-object-verb with particles marking the grammatical function of words, and sentence structure is topic-comment. Sentence-final particles are used to add emotional or emphatic impact, or make questions. Nouns have no grammatical number, gender or article aspect. Verbs are conjugated, primarily tense and voice, but not person. Japanese equivalents of adjectives are also conjugated. Japanese has a complex system of honorifics with verb forms and vocabulary to indicate the relative status of the speaker, the listener, and persons mentioned.
Japanese has no genealogical relationship with Chinese, but makes extensive use of Chinese characters, or kanji (漢字), in its writing system and a large portion of its vocabulary is borrowed from Chinese. Along with kanji, the Japanese writing system primarily uses two syllabic (or moraic) scripts, hiragana (ひらがな or 平仮名) and katakana (カタカナ or 片仮名). Latin script is used in a limited way, often in the form of rōmaji, and the numeral system uses mostly Arabic alongside traditional Chinese numerals. (source: Wikipedia)
Japanese Website Translation Basic Steps
Building a glossary: Key terminology is identified and extracted from the source files provided by the client. Upon client approval of the source terminology, it is translated and provided back to the client for review and approval. After that, the terminology is imported into a translation memory tool and updated as needed.
Make sure content is culturally correct by considering:
- Local customs
- Local content
- Morality
- Symbols
- Cultural values and social context
- Not only to translate but also “localize” (adapt) for the foreign markets
- Cultural differences
- Colors have different meanings in different countries (e.g. white means holy in the US and mourning in China)
- Cultural references or examples must be adapted to the target language or country
- Images: issues of comprehensibility and cultural appropriateness (e.g. sports represented by a football image in Argentina and a baseball image in the US)
Translation and copy writing: A professional translation service includes the accurate translation of the source text into the target language, editing of the text by a separate translation team and final proofreading by a native speaker. In order to stay true to the source content, many times this can result in translations that are more literal. Copywriting or trans-creation is required in projects that involve marketing or persuasive content, where the translated text must be then rewritten to make the message persuasive, as well as accurate and culturally appropriate. In some cases, a target language locale may be so different that a complete rewrite of source marketing text is required.
Localizing of graphics: Graphics are updated by extracting translatable text from source graphics, translating that text in the target language, and finally placing the text back into the new “translated” graphic.
Online QA: On Website localization projects, it’s essential to have language professionals examine a localized website in context ensuring all linguistic and cosmetic items are correct and the application or site works properly for the target users. Proper platforms, browsers, and test scripts are used to ensure the experience of the target user will be as good as if the application was developed specifically for that market.
Working with Content Management Systems: There are different types of multilingual web content management solutions that support the Spanish Language and website localization, including:
Having a CMS-based solution for multilingual websites reduces the number of people who handle content, which significantly reduces the chance to make a mistake. The elimination of webmaster involvement and technical expertise required by client-side authors or translation company linguists can significantly lower costs through the website translation process. For more information on multilingual CMS, please check our blog Website Localization and CMS.
Japanese Website Search Engine Optimization (SEO)

Yahoo Japan remains a very popular search engine. Majority owner, Softbank (Yahoo is a minority stakeholder), is a major player both online and through their ownership in internet infrastructure throughout the country. Your search engine optimization effort must be focused on both Yahoo Japan and Google in order to reach the majority of Japanese internet users. To optimize your website’s ranking on these engines, build a comprehensive campaign that includes the following initiatives:
- Comprehensive website translation and localization
- Multilingual keyword phrase research, refinement and localization
- Multilingual Search Engine Optimization and copy writing of main site content
- Multilingual Search Engine Optimization of meta-tags, titles, alt-tags, heading tags, HTML, etc.
- Submissions to major locale (in-country) and international Search Engines
- Website traffic and keywords ranking reporting
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaign content localization
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) country-specific campaign management
